Exploring Different Types of Hearing Aids: Pros and Con
Hearing aids come in various styles, each with its own set of pros and cons. Here’s a breakdown to help you understand which might suit you best:
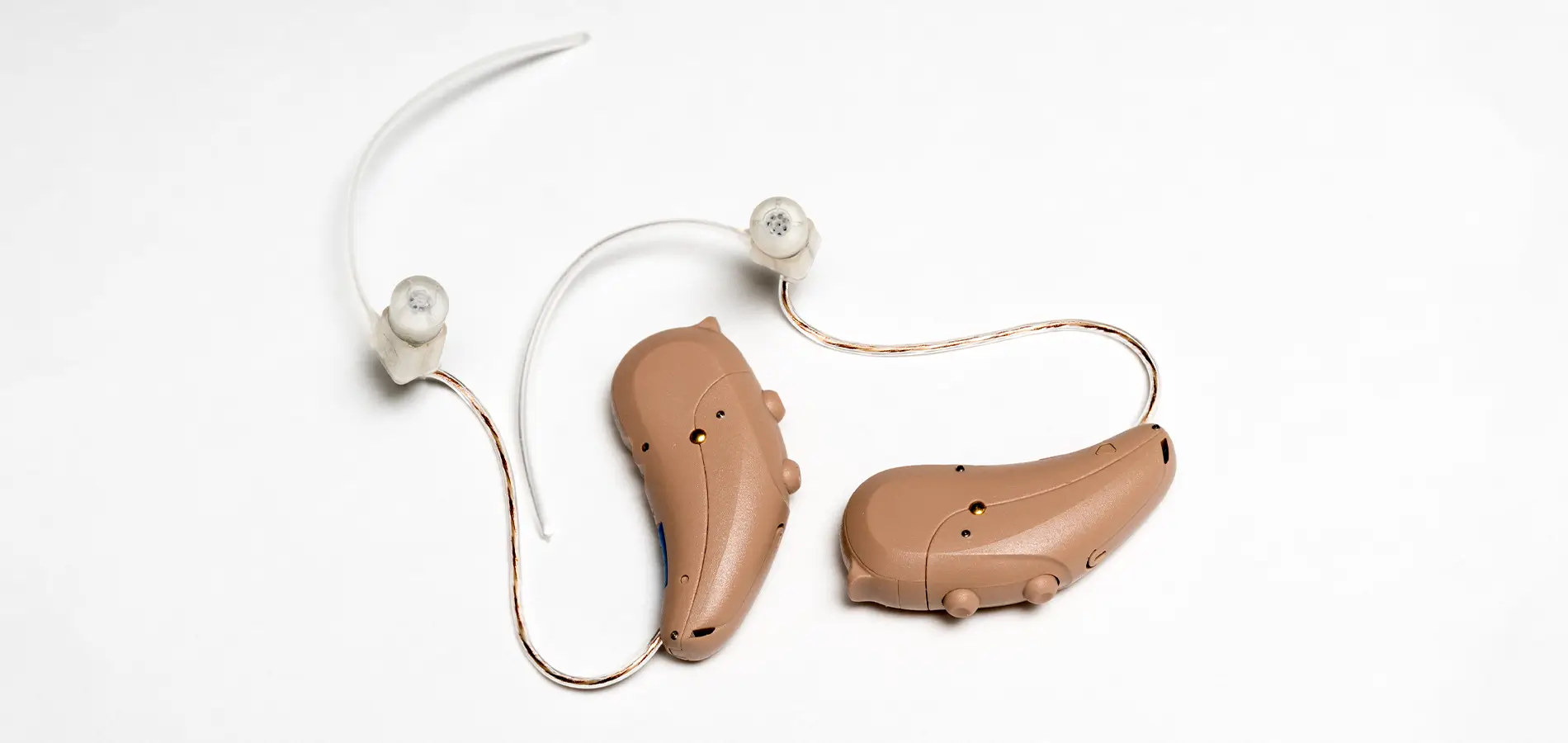
- Behind-the-Ear (BTE):
- Pros: BTEs are powerful and suitable for all types of hearing loss. They’re easy to handle and can accommodate various features like directional microphones and telecoil for phone use.
- Cons: Some users find them less discreet due to their size, though mini BTEs are smaller and more inconspicuous.
- In-the-Ear (ITE):
- Pros: ITEs are custom-made to fit your ear canal, making them comfortable and less noticeable. They’re suitable for mild to severe hearing loss.
- Cons: Their small size can limit features like directional microphones and telecoil. They may also be more prone to moisture and wax buildup.
- In-the-Canal (ITC) and Completely-in-the-Canal (CIC):
- Pros: ITC and CIC hearing aids are the smallest and least visible options. They offer cosmetic appeal and are suitable for mild to moderate hearing loss.
- Cons: Due to their size, they may not have advanced features like directional microphones. Their small batteries may also have shorter lifespan and handling can be tricky for some individuals.
- Receiver-in-Canal (RIC) or Receiver-in-the-Ear (RITE):
- Pros: RIC/RITE styles are similar to BTEs but are smaller and more discreet. They offer good sound quality and are suitable for various hearing losses.
- Cons: Some users may find them more susceptible to moisture and earwax due to the receiver being in the ear canal.
- Bone-Anchored Hearing Aids (BAHA):
- Pros: BAHA devices bypass the outer and middle ear, making them suitable for certain types of conductive or mixed hearing loss. They can provide excellent sound quality without blocking the ear canal.
- Cons: Requires a surgical procedure to implant a small titanium screw into the skull bone behind the ear. It may not be suitable for everyone, and there is a risk of infection or implant rejection.
Each type of hearing aid has its own advantages and limitations. It’s essential to consult with an audiologist to determine the most suitable option based on your hearing needs, lifestyle, and preferences.